If you have ever stepped foot in a gym, you have likely heard of creatine. For decades, it was tucked away in the lockers of bodybuilders, seen only as a tool for massive muscle growth.
As a health expert who has tracked clinical research for over twenty years, I am here to tell you that the narrative is changing. Creatine is no longer just for the gym.
It is a vital molecule for the grandmother wanting to stay mobile, the professional looking for a cognitive edge, and the woman navigating the hormonal shifts of menopause.
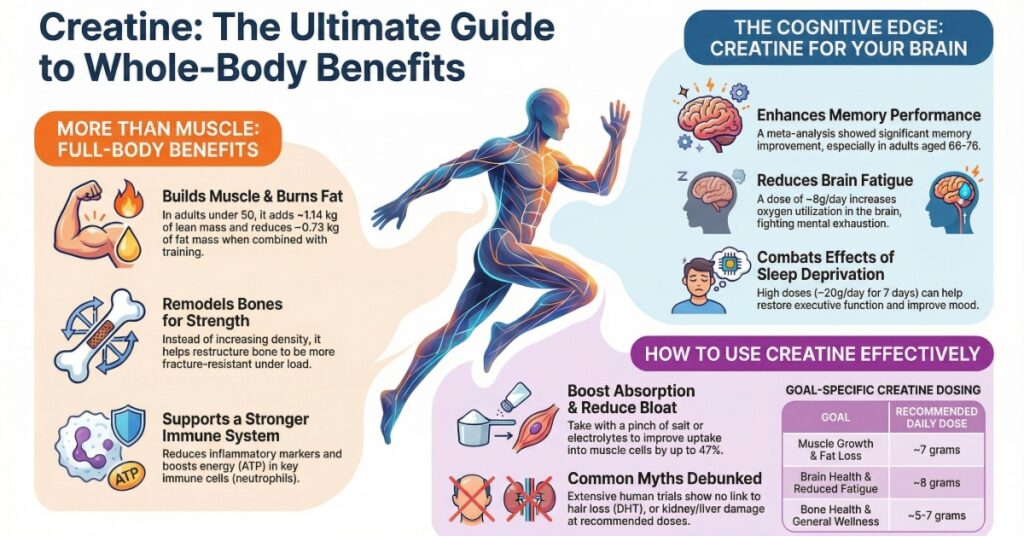
Creatine supplementation benefits include significant improvements in muscle strength, cognitive performance, and bone density by replenishing cellular energy stores known as ATP. For most adults, a daily dose of 3 to 5 grams of creatine monohydrate is the gold standard for enhancing physical and mental health across the lifespan.
What Exactly Is Creatine?
Before we dive into the “why,” let us look at the “what.” Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in your muscle cells.
It helps your muscles produce energy during heavy lifting or high intensity exercise. Think of it as a battery backup for your cells.
When your body needs a quick burst of energy, it uses a molecule called ATP. Creatine helps you recycle that energy much faster, keeping your “batteries” charged longer.
While your body produces it and you can get it from red meat, the levels are often not enough to reach “saturation.” This is why supplementation is so powerful. [1]
1. Building More Than Just “Show” Muscle
We know creatine builds muscle, but it is about more than just aesthetics. As we age, we lose muscle mass, a condition called sarcopenia.
This loss of strength is a leading cause of falls and loss of independence. Creatine helps increase lean tissue mass by improving protein synthesis. [2]
- It allows you to train harder by providing more immediate energy to the muscles.
- Studies show that even in adults under 50, combining creatine with resistance training significantly boosts strength gains. [3]
- For those over 50, the benefits are even more critical.
It helps preserve the fast-twitch muscle fibers that are responsible for power and balance. Strengthening these fibers is essential for longevity. [4]
2. A Spark Plug for Your Brain
This is perhaps the most exciting area of new research. Your brain is a massive energy consumer, using about 20% of your body’s total energy.
Just like your muscles, your brain relies on ATP to function. Recent systematic reviews have found that creatine supplementation can improve memory and executive function. [5]
This is especially true during times of “metabolic stress,” such as:
- Sleep deprivation.
- High-stress cognitive tasks.
- Natural aging.
If you feel like you are constantly in a “brain fog,” creatine might be the missing piece of your cognitive puzzle. It supports the brain’s ability to maintain energy levels during demanding mental tasks. [6]
3. Why Every Woman Should Consider Creatine
I want to speak directly to my female readers for a moment. For a long time, women avoided creatine because of the fear of “bulking up” or water retention.
The science tells a very different story. Women often have lower baseline levels of creatine in their bodies compared to men. [7]
Supplementation can be a game changer throughout a woman’s life:
- During Reproductive Years: It can help manage the energy shifts during the menstrual cycle.
- Pregnancy and Postpartum: It may support fetal development and help with postpartum recovery.
- Menopause: This is the most vital stage.
Creatine has been shown to support bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis when combined with exercise. A two-year study on postmenopausal women found that those taking creatine while exercising maintained better bone mineral density than those who did not. [8]
4. Protecting Your Body at a Cellular Level
We are now learning that creatine has systemic benefits that reach far beyond the gym floor. It appears to have a protective effect on various organs and systems.
- Immune Function: New evidence indicates that creatine can enhance the function of neutrophils, which are the “first responders” of your immune system. [9]
- Skin Health: Topical and oral creatine may protect skin cells from UV damage and oxidative stress. [10]
- Inflammation: Some studies suggest it can help lower markers of inflammation after intense physical activity. [11]
5. Debunking the Myths: Hair Loss and Kidney Health
I hear these concerns often in my clinical practice. Let us look at the facts based on the latest controlled trials.
Does it cause hair loss?
The fear of hair loss stems from one old study involving rugby players. However, modern 12-week randomized controlled trials have found no significant change in the hormones related to hair loss. [12]
Is it bad for your kidneys?
For healthy individuals, creatine is incredibly safe. Long-term studies using high doses have shown no negative impact on kidney or liver function. [13]
If you have a pre-existing kidney condition, you should speak with your doctor first. But for the general population, it is one of the most researched and safest supplements available.
How to Optimize Your Dose
You do not need complicated “loading phases” to see results. While you can take 20 grams a day for a week to saturate your muscles faster, it is often easier on the stomach to just take a steady daily dose.
- For General Health and Muscle: 3 to 5 grams per day is sufficient for most people.
- For Brain Health: Some experts suggest a slightly higher dose, perhaps 5 to 10 grams, to ensure enough crosses the blood-brain barrier. [11]
- For Older Adults: If you are over 50, aiming for the 5 to 7 gram range might be more effective as our receptors become less efficient. [4]
The Best Form: Always stick with Creatine Monohydrate. It is the most studied, most effective, and most affordable form on the market. [1]
Final Thoughts on Total Body Health
Creatine monohydrate is inexpensive, safe, and effective. It is one of the few supplements that lives up to the hype.
Whether you are 25 and trying to hit a personal record or 65 and trying to stay sharp and fracture-resistant, it is a foundational tool. It supports the very energy systems that keep us alive and vibrant.
- Choose Monohydrate: It is the most researched and cost-effective form.
- Add Sodium (aka The Sodium Hack): Use a pinch of salt to maximize absorption.
- Stay Consistent: Daily use is required to maintain cellular stores.
By viewing creatine as a “whole-body” essential, you can unlock better physical strength, sharper mental clarity, and a more resilient immune system.
Sources and References
- Creatine in Health and Disease. Nutrients, 2021.
- The Effect of Creatine Supplementation on Resistance Training-Based Changes to Body Composition. PubMed, 2022.
- Effects of Creatine Supplementation and Resistance Training on Muscle Strength Gains in Adults <50 Years of Age. PMC, 2024.
- Meta-Analysis Examining the Importance of Creatine Ingestion Strategies on Lean Tissue Mass and Strength in Older Adults. PubMed, 2021.
- Effects of Creatine Supplementation on Memory in Healthy Individuals: A Systematic Review. PubMed, 2023.
- Effects of Creatine Supplementation on Brain Function and Health. PubMed, 2021.
- Creatine Supplementation in Women’s Health: A Lifespan Perspective. PMC, 2021.
- A 2-yr Randomized Controlled Trial on Creatine Supplementation during Exercise for Postmenopausal Bone Health. PubMed, 2023.
- Creatine Supplementation Enhances Immunological Function of Neutrophils. PMC, 2022.
- The Creatine Kinase System in Human Skin: Protective Effects Against Oxidative Damage. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2005.
- This Powder Drops Inflammation, Shrinks Fat and Builds Serious Muscle. Clinical Review, 2024.
- Does Creatine Cause Hair Loss? A 12-week Randomized Controlled Trial. PMC, 2025.
- Effects of High-Dose Creatine Supplementation on Kidney and Liver Responses. PMC, 2009.
Disclaimer: The content in this playlist is for informational and educational purposes only. Fasting is a powerful biological tool. Always consult with your healthcare professional before beginning a new fasting protocol, especially if you have a pre-existing medical condition or are taking medication.